Poiesis Architecture
INFO
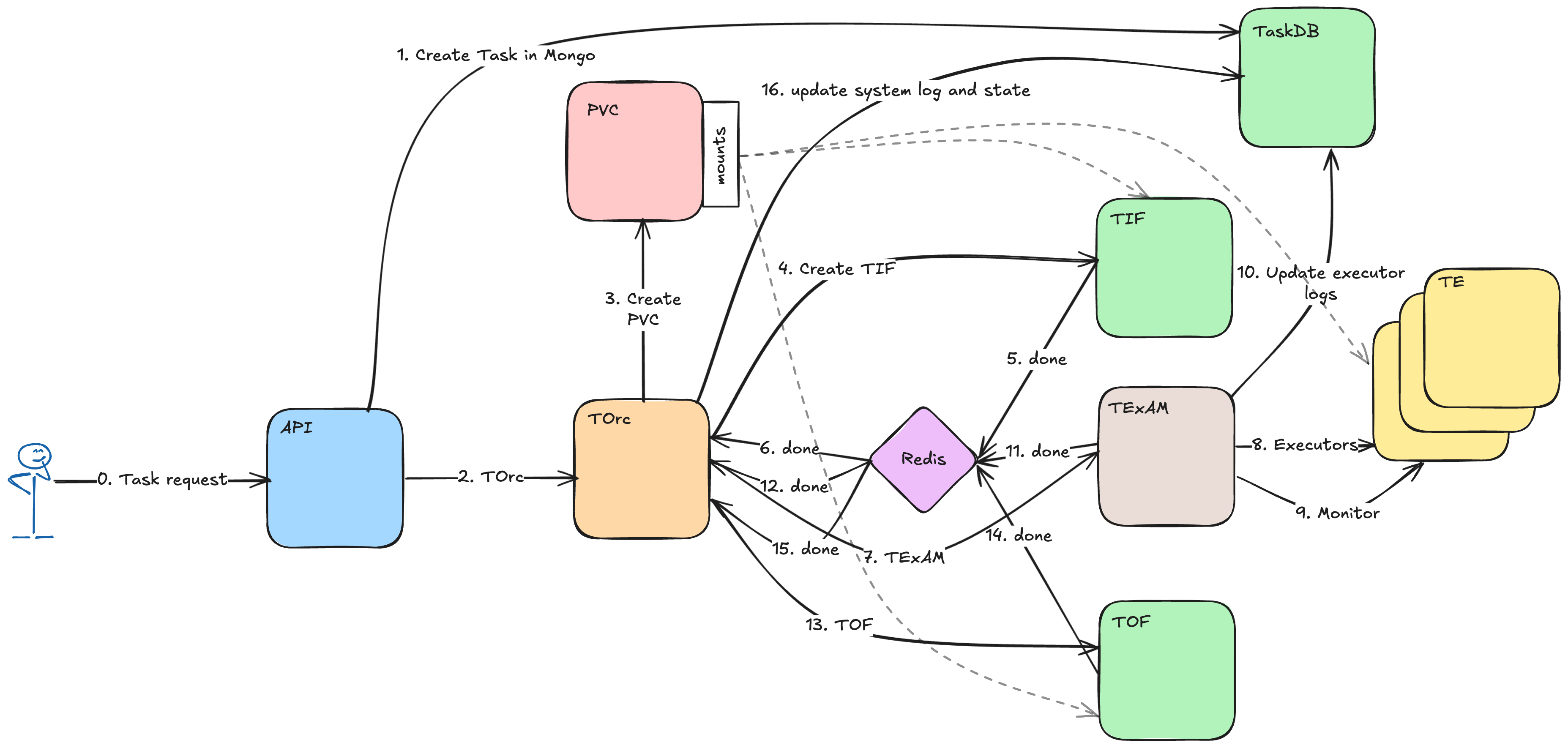
The above diagram shows the flow of task creation in Poiesis, its not verbatim but gives a high level overview of the process.
Initialization:
- The User submits a task request to the API.
- The API generates a unique ID (UUID) for the task and creates a corresponding record in MongoDB (
TaskDB). This database entry is the central source of information for the task state. - Once the task is persisted in the database, the API triggers the creation of the main
TorcJob in Kubernetes.
Data Preparation:
Torcfirst requests the creation of a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) as specified by the user.Torcthen launches a sub-job/pod calledTIF(Task Input Fetcher).TIFdownloads the necessary input data and mounts/places it onto the PVC.- Upon completion,
TIFsends a message to a task-specific Redis Channel indicating that the input data is ready. Torclistens to this channel and proceeds once notified.
Execution:
TorclaunchesTExAM(Task Executor And Monitor).TExAMis responsible for creating and launching the actual Task Executor pods (TE).TExAMensures the data from the PVC (both input and space for output) is correctly mounted into the Task Executor pods.TExAMmonitors the lifecycle of all Task Executor pods.- The Task Executor pods perform the core work, reading input from and writing output to the PVC.
- Once all Task Executors have finished,
TExAMsignals completion via the Redis Channel. Torcreceives this notification.
Data Output:
Torclaunches the final sub-job/pod,TOF(Task Output Fetcher).TOFreads the resulting output data generated by the Task Executors from the PVC.TOFuploads this data to the final User Output Location specified in the initial request.
Status and Logging (Ongoing):
- Throughout the process, both
TorcandTExAMperiodically update the task's status and relevant logs (system logs, executor logs) in the central MongoDB (TaskDB).
- Throughout the process, both